Power in terms of international relations has traditionally been defined and assessed in terms of military and economic might, which is generally referred to as hard power. But recently it can be seen that soft power is increasingly becoming the driving force behind a nation’s global authority and financial gain as countries grow more linked. The concept of soft power was first created by political scientist Joseph Nye to describe a country’s ability to influence others gently without force or intimidation, but utilizing culture, politics, and institutions. But with recent digital technologies and connectivity, things like music, food, media, sports, films, and other cultural exports can be wielded as soft power by a nation.
Soft Power and Creative Economy
The term creative economy was first coined by John Howkins in 2001 in his book – ‘The Creative Economy: How People Make Money From Ideas’. Creative economy, also known as orange economy, is an evolving concept which is based on the contribution and potential of creative assets to contribute to economic growth and development. This concept came out after recognizing the importance of creative industries which consist of soft powers like theatre, dance, fashion, music, food, media, games, and the heritage sector. In recent times, with the use of digital technologies, creative economy has contributed quite a bit towards the economy and created millions of jobs.
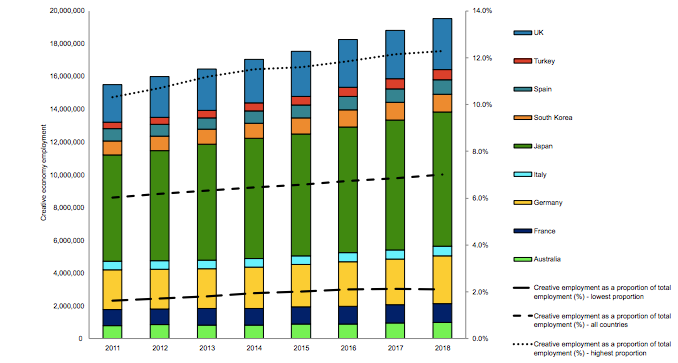
In the twenty-first century, the ability of nations to expand their global reach and further their economic goals has slowly grown dependent on soft power. The culture that produces a creative economy consisting of cultural goods as well as creative expression has developed into an extremely successful method of utilizing and expanding soft power. Also with the increase in the use of digital technologies to create and share contents, creative economy has contributed quite a bit towards the economy and created millions of jobs. According to a Deloitte report, the creative economy plays a significant role in developed nations by employing almost 20 million individuals across nine studied economies as shown in Figure 1, making up over 7% of total employment in those countries with some countries seeing it as high as nearly 13%. Importantly, the creative economy has been consistently growing in all countries studied, adding about 4 million jobs from 2011 to 2018.
Figure 1: Creative Economy Size from 2011-2018 AD with Total and % of Total Employment in Nine Countries
Source: Deloitte Report
South Korea: An Emerging Soft Power and Creative Economy Hub
In recent years, South Korea’s cultural exports, such as K-pop, K-beauty, and Korean cuisine, have gained immense popularity worldwide. This phenomenon, known as the ‘Korean Wave’ or ‘Hallyu’, has contributed to the country’s global standing and soft power projection and has led to significant economic growth in South Korea. According to Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA), the creative economy recorded a total of USD 52.8 billion in sales in the first half of 2023, which is a 2.5% increase compared to the same period the previous year.
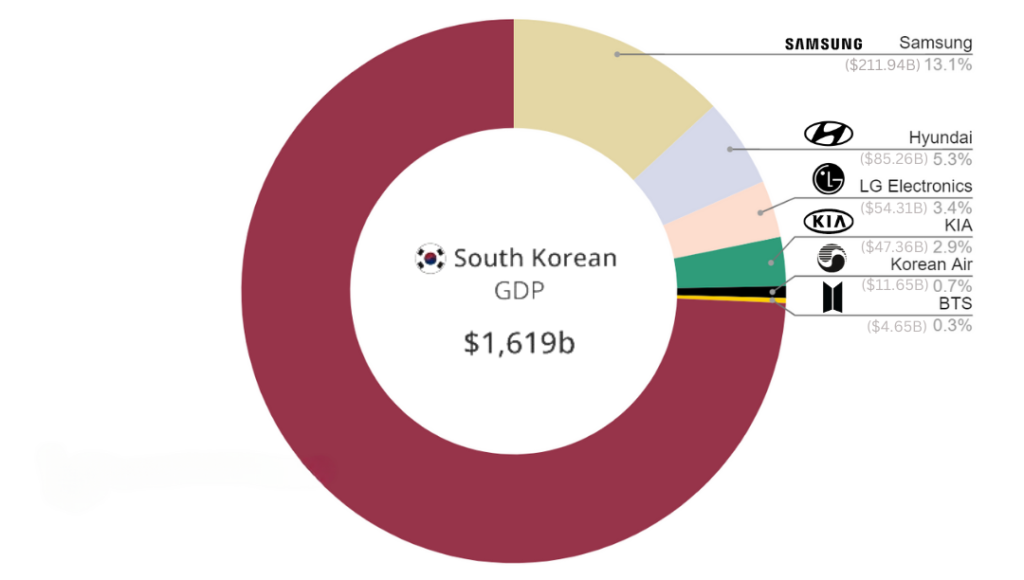
Music, films, fashion, and beauty products are the key drivers of the creative economy, especially the globally renowned K-pop boy band – BTS, has contributed quite a bit. In 2018, BTS alone contributed USD 4.65 billion to South Korea’s economy which represented 0.3% of the total GDP, putting them on the list with major corporations like Samsung, Hyundai and Korean Air as shown in Figure 2. Other than BTS, we have many more K-pop bands like Seventeen, Blackpink, and Straykids who have also contributed to taking the South Korean music industry to the international stage, attracting billions of fans and generating revenue streams for the nation.
Other than K-pop, K-beauty products and K-cuisine has also taken the world by storm. According to International Trade Administration (ITA), South Korea was the third largest exporter in the cosmetics market after France and United States, with exports reaching around USD 7.8 billion in 2021. Similarly, South Korea’s cuisine has also captured international attention, with Korean restaurants being opened in major cities worldwide. With the increased popularity and influence of these soft powers, the government of South Korea has also acknowledged its importance and use by supporting initiatives such as the Korean Cultural Centers and cultural exchange programs which has facilitated greater cultural exchange and cooperation between South Korea and other nations. Additionally, institutions like KOCCA and the Korea Foundation for International Culture Exchange (KOFICE) play pivotal roles in promoting South Korean culture and creative industries internationally.
Figure 2: Contribution of BTS and Other Selected Companies/Entities in South Korean GDP in 2018 AD
Source: Statista
Taylor Swift’s Influence on Singapore
Taylor Swift is one of the best-selling music artists with a massive global following. Her concerts not only provide entertainment but also boost the economies of the cities where she performs. This was clearly seen in Singapore during her recent ‘The Eras Tour’ in March 2024. With Singapore being the only Southeast Asian stop on her tour, the country saw a big economic boost. Taylor Swift performed six shows in Singapore attracting fans from all over Southeast Asia, especially from countries like Thailand, Malaysia, and the Philippines. The tickets were sold out as soon as it was released almost a year ago in July 2023. With over 300,000 tickets sold, it was estimated that Singapore’s economy would boost to about USD 300 million to USD 400 million, which would make up to 0.2% of Singapore’s GDP in the first quarter. At the same time, along with the tickets, demand for air flights and hotels also skyrocketed for March 2024. In July 2023 after the ticket sales, the hotel occupancy also saw an increase of 10% in their occupancy. Marina Bay Sands, a luxury hotel and tourism destination in Singapore, introduced their own packages ranging from USD 7,500 to USD 35,00 which were all sold out. The economic benefits of Taylor Swift’s concert went beyond tourism with restaurants, bars, ride-sharing services, and shops also saw increased business as fans ate, shopped, and explored the city’s attractions. Thus, the Taylor Swift concert not only increased Singapore’s economy but also brought positive attention to Singapore itself.
Outlook
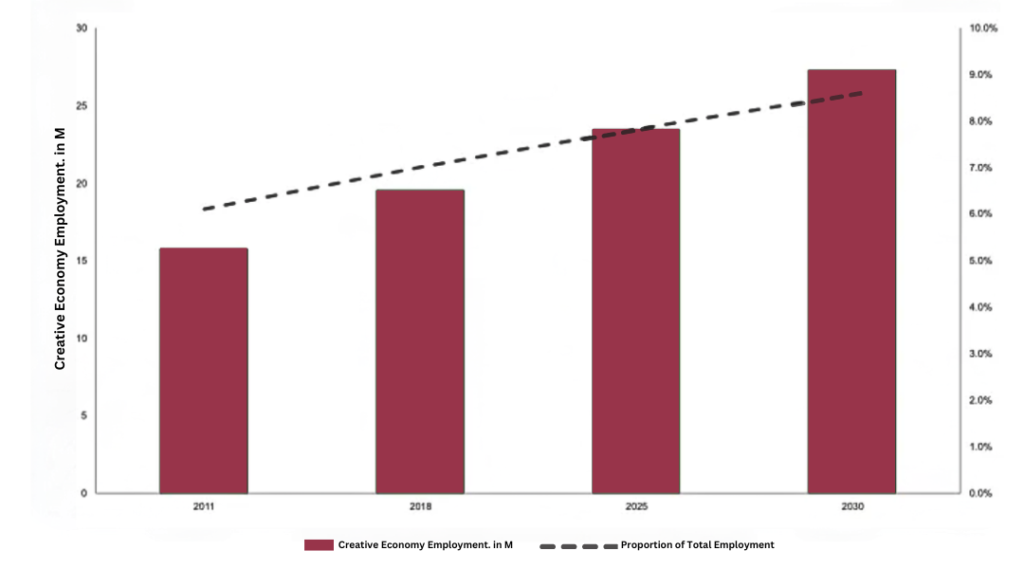
Creative economy driven by soft power plays an important role in shaping a nation’s global influence and economy. All countries are realizing the potential and the influence of the creative economy which can also be seen in the forecast where the creative economy employment is to increase by about 4% from 2011 to 2030 as shown in figure below.
Figure 3: Creative Economy Size Forecast 2011-2030 AD with Total and % of Total Employment in Nine Countries
Source: Deloitte Report
From K-pop’s cultural phenomenon to Taylor Swift’s economic impact, these are some examples of how soft power drives economic growth and enhances global standing. By harnessing their unique cultural assets and embracing sustainability, nations can make use of the creative economy effectively. Moreover, a culturally rich country like Nepal can unlock their soft power potential and seize opportunities for growth and development on the world stage. We can utilize our diverse traditional cultural dances and food to appeal to the global audience. Investing in the preservation and promotion of Nepal’s cultural heritage, including its music, art, and cuisine, can enhance the country’s soft power projection. Recently, momo has been trending with the help of various social medias like Instagram and Youtube, especially in India, so if Nepal is able to market and utilize the momo then Nepal can increase its economy along with the global standing. Whether through music, film, cuisine, or beauty products, the creative economy and soft power helps to interconnect and transcend borders.
Anushka Shrestha graduated with a Bachelor's degree in Business Administration (International Hotel Management) from Stamford International University, Thailand. Her interest lies in tourism, hospitality and sustainable businesses. Currently, she works as a Research Fellow at Nepal Economic Forum (NEF).